| Year |
Balance |
| 0 |
$10,000 |
| 1 |
$10,500 |
| 2 |
$11,025 |
| 3 |
$11,576.25 |
| 4 |
$12,155.06 |
| 5 |
$12,762.82 |
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | A class to monitor the growth of an investment that |
| 3 | accumulates interest at a fixed annual rate |
| 4 | */ |
| 5 | public class Investment |
| 6 | { |
| 7 | /** |
| 8 | Constructs an Investment object from a starting balance and |
| 9 | interest rate. |
| 10 | @param aBalance the starting balanece |
| 11 | @param aRate the interest rate in percent |
| 12 | */ |
| 13 | public Investment(double aBalance, double aRate) |
| 14 | { |
| 15 | balance = aBalance; |
| 16 | rate = aRate; |
| 17 | years = 0; |
| 18 | } |
| 19 | |
| 20 | /** |
| 21 | Keeps accumulating interest until a target balance has |
| 22 | been reached. |
| 23 | @param targetBalance the desired balance |
| 24 | */ |
| 25 | public void waitForBalance(double targetBalance) |
| 26 | { |
| 27 | while (balance < targetBalance) |
| 28 | { |
| 29 | years++; |
| 30 | double interest = balance * rate / 100; |
| 31 | balance = balance + interest; |
| 32 | } |
| 33 | } |
| 34 | |
| 35 | /** |
| 36 | Gets the current investment balance. |
| 37 | @return the current balance |
| 38 | */ |
| 39 | public double getBalance() |
| 40 | { |
| 41 | return balance; |
| 42 | } |
| 43 | |
| 44 | /** |
| 45 | Gets the number of years this investment has accumulated |
| 46 | interest. |
| 47 | @return the number of years since the start of the investment |
| 48 | */ |
| 49 | public int getYears() |
| 50 | { |
| 51 | return years; |
| 52 | } |
| 53 | |
| 54 | private double balance; |
| 55 | private double rate; |
| 56 | private int years; |
| 57 | } |
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | This program computes how long it takes for an investment |
| 3 | to double. |
| 4 | */ |
| 5 | public class InvestmentTest |
| 6 | { |
| 7 | public static void main(String[] args) |
| 8 | { |
| 9 | final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 10000; |
| 10 | final double RATE = 5; |
| 11 | Investment invest = new Investment(INITIAL_BALANCE, RATE); |
| 12 | invest.waitForBalance(2 * INITIAL_BALANCE); |
| 13 | int years = invest.getYears(); |
| 14 | System.out.println("The investment doubled after " |
| 15 | + years + " years"); |
| 16 | } |
| 17 | } |
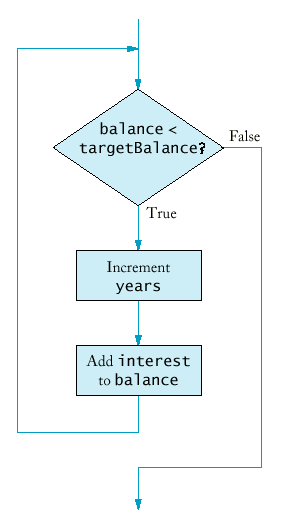
Example:
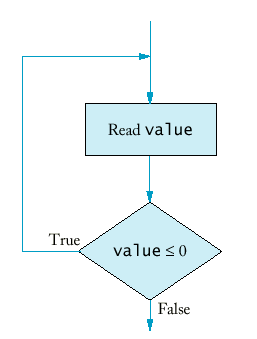
Purpose:To execute a statement while a condition is true |
do
statement
while (condition);
Example: Validate input
double value;
do
{
String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(
"Please enter a positive number");
value = Integer.parseInt(input);
}
while (input <= 0);
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | A class to monitor the growth of an investment that |
| 3 | accumulates interest at a fixed annual rate |
| 4 | */ |
| 5 | public class Investment |
| 6 | { |
| 7 | /** |
| 8 | Constructs an Investment object from a starting balance and |
| 9 | interest rate. |
| 10 | @param aBalance the starting balanece |
| 11 | @param aRate the interest rate in percent |
| 12 | */ |
| 13 | public Investment(double aBalance, double aRate) |
| 14 | { |
| 15 | balance = aBalance; |
| 16 | rate = aRate; |
| 17 | years = 0; |
| 18 | } |
| 19 | |
| 20 | /** |
| 21 | Keeps accumulating interest until a target balance has |
| 22 | been reached. |
| 23 | @param targetBalance the desired balance |
| 24 | */ |
| 25 | public void waitForBalance(double targetBalance) |
| 26 | { |
| 27 | while (balance < targetBalance) |
| 28 | { |
| 29 | years++; |
| 30 | double interest = balance * rate / 100; |
| 31 | balance = balance + interest; |
| 32 | } |
| 33 | } |
| 34 | |
| 35 | /** |
| 36 | Keeps accumulating interest for a given number of years. |
| 37 | @param n the number of years |
| 38 | */ |
| 39 | public void waitYears(int n) |
| 40 | { |
| 41 | for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) |
| 42 | { |
| 43 | double interest = balance * rate / 100; |
| 44 | balance = balance + interest; |
| 45 | } |
| 46 | years = years + n; |
| 47 | } |
| 48 | |
| 49 | /** |
| 50 | Gets the current investment balance. |
| 51 | @return the current balance |
| 52 | */ |
| 53 | public double getBalance() |
| 54 | { |
| 55 | return balance; |
| 56 | } |
| 57 | |
| 58 | /** |
| 59 | Gets the number of years this investment has accumulated |
| 60 | interest. |
| 61 | @return the number of years since the start of the investment |
| 62 | */ |
| 63 | public int getYears() |
| 64 | { |
| 65 | return years; |
| 66 | } |
| 67 | |
| 68 | private double balance; |
| 69 | private double rate; |
| 70 | private int years; |
| 71 | } |
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | This program computes how much an investment grows in |
| 3 | a given number of years. |
| 4 | */ |
| 5 | public class InvestmentTest |
| 6 | { |
| 7 | public static void main(String[] args) |
| 8 | { |
| 9 | final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 10000; |
| 10 | final double RATE = 5; |
| 11 | final int YEARS = 20; |
| 12 | Investment invest = new Investment(INITIAL_BALANCE, RATE); |
| 13 | invest.waitYears(YEARS); |
| 14 | double balance = invest.getBalance(); |
| 15 | System.out.println("The balance after " + YEARS + |
| 16 | " years is " + balance); |
| 17 | } |
| 18 | } |
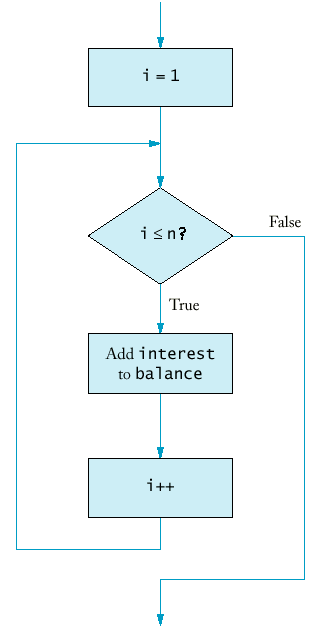
Example:
Purpose:To execute an initialization, then keep executing a statement and updating an expression while a condition is true |
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | This class describes triangle objects that can be displayed |
| 3 | as shapes like this: |
| 4 | [] |
| 5 | [][] |
| 6 | [][][] |
| 7 | */ |
| 8 | public class Triangle |
| 9 | { |
| 10 | /** |
| 11 | Constructs a triangle. |
| 12 | @param aWidth the number of [] in the last row of the triangle. |
| 13 | */ |
| 14 | public Triangle(int aWidth) |
| 15 | { |
| 16 | width = aWidth; |
| 17 | } |
| 18 | |
| 19 | /** |
| 20 | Computes a string representing the triangle. |
| 21 | @return a string consisting of [] and newline characters |
| 22 | */ |
| 23 | public String toString() |
| 24 | { |
| 25 | String r = ""; |
| 26 | for (int i = 1; i <= width; i++) |
| 27 | { |
| 28 | // make triangle row |
| 29 | for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) |
| 30 | r = r + "[]"; |
| 31 | r = r + "\n"; |
| 32 | } |
| 33 | return r; |
| 34 | } |
| 35 | |
| 36 | private int width; |
| 37 | } |
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | This program tests the Triangle class. |
| 3 | */ |
| 4 | public class TriangleTest |
| 5 | { |
| 6 | public static void main(String[] args) |
| 7 | { |
| 8 | Triangle small = new Triangle(3); |
| 9 | System.out.println(small.toString()); |
| 10 | |
| 11 | Triangle large = new Triangle(15); |
| 12 | System.out.println(large.toString()); |
| 13 | } |
| 14 | } |
boolean done = false;
while (!done)
{
String input = read input;
if (end of input indicated)
done = true;
else
{
process input
}
}
"Loop and a half"
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | Computes the average of a set of data values. |
| 3 | */ |
| 4 | public class DataSet |
| 5 | { |
| 6 | /** |
| 7 | Constructs an empty data set. |
| 8 | */ |
| 9 | public DataSet() |
| 10 | { |
| 11 | sum = 0; |
| 12 | count = 0; |
| 13 | maximum = 0; |
| 14 | } |
| 15 | |
| 16 | /** |
| 17 | Adds a data value to the data set |
| 18 | @param x a data value |
| 19 | */ |
| 20 | public void add(double x) |
| 21 | { |
| 22 | sum = sum + x; |
| 23 | if (count == 0 || maximum < x) maximum = x; |
| 24 | count++; |
| 25 | } |
| 26 | |
| 27 | /** |
| 28 | Gets the average of the added data. |
| 29 | @return the average or 0 if no data has been added |
| 30 | */ |
| 31 | public double getAverage() |
| 32 | { |
| 33 | if (count == 0) return 0; |
| 34 | else return sum / count; |
| 35 | } |
| 36 | |
| 37 | /** |
| 38 | Gets the largest of the added data. |
| 39 | @return the maximum or 0 if no data has been added |
| 40 | */ |
| 41 | public double getMaximum() |
| 42 | { |
| 43 | return maximum; |
| 44 | } |
| 45 | |
| 46 | private double sum; |
| 47 | private double maximum; |
| 48 | private int count; |
| 49 | } |
| 1 | import javax.swing.JOptionPane; |
| 2 | |
| 3 | /** |
| 4 | This program computes the average and maximum of a set |
| 5 | of input values. |
| 6 | */ |
| 7 | public class InputTest |
| 8 | { |
| 9 | public static void main(String[] args) |
| 10 | { |
| 11 | DataSet data = new DataSet(); |
| 12 | |
| 13 | boolean done = false; |
| 14 | while (!done) |
| 15 | { |
| 16 | String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter value, Cancel to quit"); |
| 17 | if (input == null) |
| 18 | done = true; |
| 19 | else |
| 20 | { |
| 21 | double x = Double.parseDouble(input); |
| 22 | data.add(x); |
| 23 | } |
| 24 | } |
| 25 | |
| 26 | System.out.println("Average = " + data.getAverage()); |
| 27 | System.out.println("Maximum = " + data.getMaximum()); |
| 28 | } |
| 29 | } |
StringTokenizer tokenizer
= new StringTokenizer();
while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens())
{
String token = tokenizer.nextToken();
process token
}
| 1 | import java.util.StringTokenizer; |
| 2 | import javax.swing.JOptionPane; |
| 3 | |
| 4 | /** |
| 5 | This program computes the average and maximum of a set |
| 6 | of input values that are entered on a single line. |
| 7 | */ |
| 8 | public class InputTest |
| 9 | { |
| 10 | public static void main(String[] args) |
| 11 | { |
| 12 | DataSet data = new DataSet(); |
| 13 | |
| 14 | String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter values:"); |
| 15 | StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(input); |
| 16 | while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) |
| 17 | { |
| 18 | String token = tokenizer.nextToken(); |
| 19 | |
| 20 | double x = Double.parseDouble(token); |
| 21 | data.add(x); |
| 22 | } |
| 23 | |
| 24 | System.out.println("Average = " + data.getAverage()); |
| 25 | System.out.println("Maximum = " + data.getMaximum()); |
| 26 | } |
| 27 | } |
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
char ch = s.charAt(i);
process ch
}
int vowelCount = 0;
String vowels = "aeiouy";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (vowels.indexOf(ch) >= 0)
vowelCount++;
}
| 1 | import java.util.Random; |
| 2 | |
| 3 | /** |
| 4 | This class models a die that, when cast, lands on a random |
| 5 | face. |
| 6 | */ |
| 7 | public class Die |
| 8 | { |
| 9 | /** |
| 10 | Constructs a die with a given number of sides |
| 11 | @param s the number of sides, e.g. 6 for a normal die |
| 12 | */ |
| 13 | public Die(int s) |
| 14 | { |
| 15 | sides = s; |
| 16 | generator = new Random(); |
| 17 | } |
| 18 | |
| 19 | /** |
| 20 | Simulates a throw of the die |
| 21 | @return the face of the die |
| 22 | */ |
| 23 | public int cast() |
| 24 | { |
| 25 | return 1 + generator.nextInt(sides); |
| 26 | } |
| 27 | |
| 28 | |
| 29 | private Random generator; |
| 30 | private int sides; |
| 31 | } |
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | This program simulates casting a die ten times. |
| 3 | */ |
| 4 | public class DieTest |
| 5 | { |
| 6 | public static void main(String[] args) |
| 7 | { |
| 8 | Die d = new Die(6); |
| 9 | final int TRIES = 10; |
| 10 | for (int i = 1; i <= TRIES; i++) |
| 11 | { |
| 12 | int n = d.cast(); |
| 13 | System.out.print(n + " "); |
| 14 | } |
| 15 | System.out.println(); |
| 16 | } |
| 17 | } |
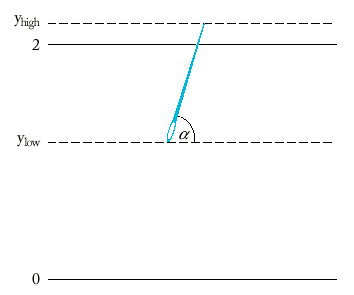
| 1 | import java.util.Random; |
| 2 | |
| 3 | /** |
| 4 | This class simulates a needle in the Buffon needle experiment. |
| 5 | */ |
| 6 | public class Needle |
| 7 | { |
| 8 | /** |
| 9 | Constructs a needle. |
| 10 | */ |
| 11 | public Needle() |
| 12 | { |
| 13 | hits = 0; |
| 14 | generator = new Random(); |
| 15 | } |
| 16 | |
| 17 | /** |
| 18 | Drops the needle on the grid of lines and |
| 19 | remembers whether the needle hit a line. |
| 20 | */ |
| 21 | public void drop() |
| 22 | { |
| 23 | double ylow = 2 * generator.nextDouble(); |
| 24 | double angle = 180 * generator.nextDouble(); |
| 25 | |
| 26 | // compute high point of needle |
| 27 | |
| 28 | double yhigh = ylow + Math.sin(Math.toRadians(angle)); |
| 29 | if (yhigh >= 2) hits++; |
| 30 | tries++; |
| 31 | } |
| 32 | |
| 33 | /** |
| 34 | Gets the number of times the needle hit a line. |
| 35 | @return the hit count |
| 36 | */ |
| 37 | public int getHits() |
| 38 | { |
| 39 | return hits; |
| 40 | } |
| 41 | |
| 42 | /** |
| 43 | Gets the total number of times the needle was dropped. |
| 44 | @return the try count |
| 45 | */ |
| 46 | public int getTries() |
| 47 | { |
| 48 | return tries; |
| 49 | } |
| 50 | |
| 51 | private Random generator; |
| 52 | private int hits; |
| 53 | private int tries; |
| 54 | } |
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | This program simulates the Buffon needle experiment |
| 3 | and prints the resulting approximations of pi. |
| 4 | */ |
| 5 | public class NeedleTest |
| 6 | { |
| 7 | public static void main(String[] args) |
| 8 | { |
| 9 | Needle n = new Needle(); |
| 10 | final int TRIES1 = 10000; |
| 11 | final int TRIES2 = 100000; |
| 12 | |
| 13 | for (int i = 1; i <= TRIES1; i++) |
| 14 | n.drop(); |
| 15 | System.out.println("Tries / Hits = " |
| 16 | + (double)n.getTries() / n.getHits()); |
| 17 | |
| 18 | for (int i = TRIES1 + 1; i <= TRIES2; i++) |
| 19 | n.drop(); |
| 20 | System.out.println("Tries / Hits = " |
| 21 | + (double)n.getTries() / n.getHits()); |
| 22 | } |
| 23 | } |